
Green Methanol Emerging as Key Player in Renewable Energy Transition
- Green methanol demand spikes amid intensified climate initiatives, offering up to 99% emission reductions.
- North America leads in expanding production capacity, driven by significant industry collaborations.
- This fuel is becoming essential for enhancing renewable energy storage solutions.
July 30, 2024 | Chemicals 3 minutes read
Amid the intensifying fight against climate change, the demand for sustainable fuels with minimal to no emissions is at an all-time high. One of the viable options is green methanol.
Green methanol dramatically reduces CO2, NOx, SOx, and other emissions by 60-99%. When considering the carbon footprint from production to utilization, green methanol is the most sustainable alternative to conventional fuels.
Green methanol is divided into bio-methanol and e-methanol. Bio-methanol is produced by gasification or pyrolysis technology, while e-methanol uses electrolysis technology. Both methods are followed by a catalytic reaction process to produce methanol.
Uses of Green Methanol
Transportation:
Green methanol offers a clean-burning alternative for various vehicles, from ships to buses, significantly reducing harmful emissions and improving air quality.
Sustainable Materials:
Green methanol serves as a sustainable source for manufacturing everyday items, such as plastics, paints, textiles, and construction materials, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Energy Storage:
Green methanol's storage and transport capabilities enable effective utilization of renewable energy by converting surplus solar or wind power into green hydrogen and subsequently into green methanol for future use or electricity generation.
Current and Upcoming Green Methanol Projects
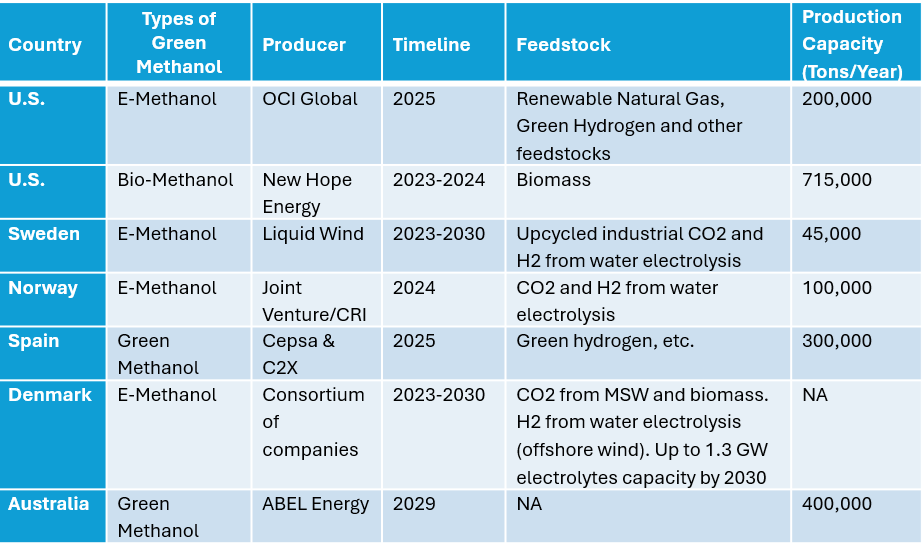
Global methanol demand increased to 126 million tons in 2023, with global capacity reaching just short of 170 million tons per year in 2023. Total global green methanol capacity is estimated at 536 thousand tons in 2023, an increase from 390 thousand tons in 2022.
North America is currently leading in green methanol production with around 75%, followed by Europe (15%), Asia (9.7%), and South America (0.2%).
However, there are multiple green methanol plants under construction or in planning phases throughout the globe, which will increase the total production capacity by the end of this decade.
According to the Methanol Institute, the total projected capacity of all e-methanol projects is anticipated to be 11.6 million tons by 2027 and 15.0 million tons by 2029. The total capacity of all bio-methanol projects is expected to be 7.7 million tons and 9.2 million tons during the same periods.
Recently, the methanol industry has witnessed significant collaboration aimed at sustainability goals.
Elyse Energy, known for its expertise in low-carbon molecule production, and Lhyfe, a global leader in green hydrogen production, have formed a strategic partnership. Their joint effort focuses on advancing the production of e-methanol from green hydrogen within the industrial and logistical port ecosystem of the Loire Estuary.
Another collaboration took place between Methanex, a prominent global producer of methanol, and Entropy, a frontrunner in carbon capture and storage technology.
This collaboration combines Entropy's proficiency in carbon capture with Methanex's deep knowledge of methanol production. A segment of the captured CO2 will be employed to optimize methanol production, highlighting the role of these Canadian firms in pioneering low-carbon solutions.
Conclusion
While green methanol may not be the definitive solution, it represents a significant advancement in available resources. This fuel offers cleaner combustion, supporting the transportation and industrial sectors while providing a more sustainable method for producing everyday goods. Additionally, its ability to store renewable energy introduces a valuable new dimension.
Author: Vismay Kakhandki



